Table of Contents
This article is an analysis of the network event loops based on bitcoin core v0.19.0.
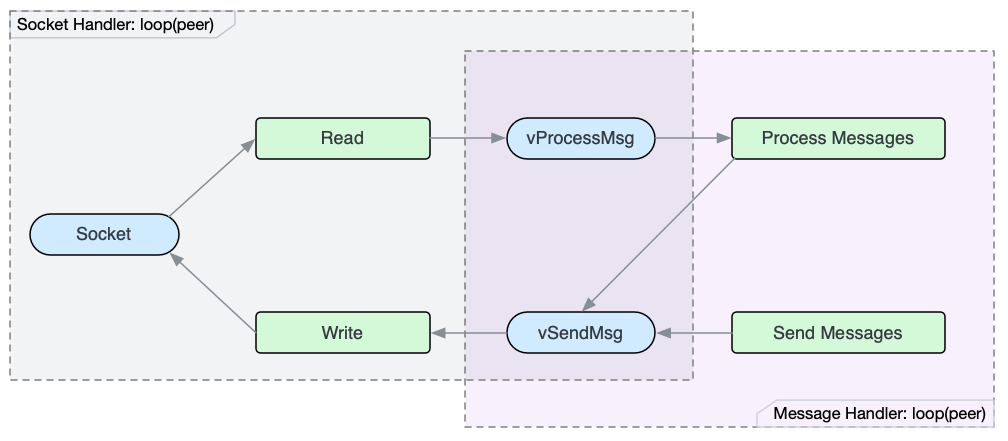
Bitcoin starts two threads to handle network messages, and each thread runs its own event loop.
Socket Handler Thread
The Socket Handler Thread is responsible for the underlying socket IO.
It loops each connected peer in a round-robin schedule. The handler reads messages from the peer socket into the receiving queue vProcessMsg, and sends message in the sending queue vSendMsg to peer.
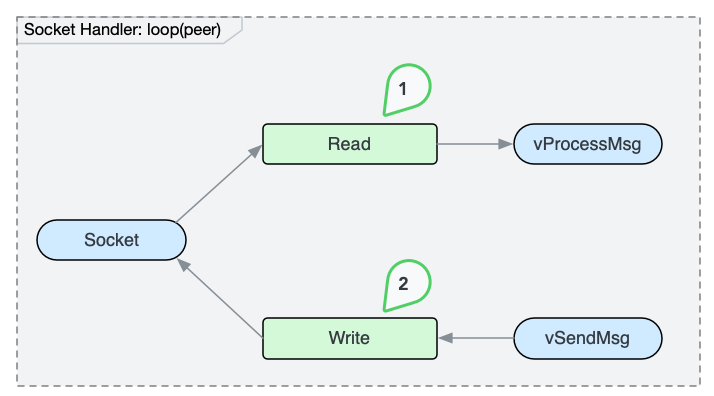
Read from Socket
First, the thread tries to read some data from current peer.
- Read some data from socket.
- Decode the message. The newly decoded messages are stored in a queue named
vRecvMsg. - Move the decoded message in
vRecvMsgto another queuevProcessMsg. The queuevProcessMsgis the inbox for the Message Handler Thread. - If there is any new decoded message in this loop step, try to wake the Message Handler Thread.
Write to Socket
Then, the thread sends queued messages in vSendMsg to current peer.
Code References
CConnman::Start: This is the main entry to start network threads.CConnman::SocketHandler: The main logic of Socket Handler Thread.CNode::ReceiveMsgBytes: Decode received bytes into message.
Message Handler Thread
Message Handler Thread handles the network messages without worrying the socket operations.
The behavior of the Message Handler Thread is similar to the Socket Handler Thread. Both loops each connected peer in the round-robin way. And for each peer, they first process incoming messages, and then send outgoing messages. The difference is that Message Handler Thread reads messages from the queue vProcessMsg and queues outgoing messages in the queue vSendMsg.
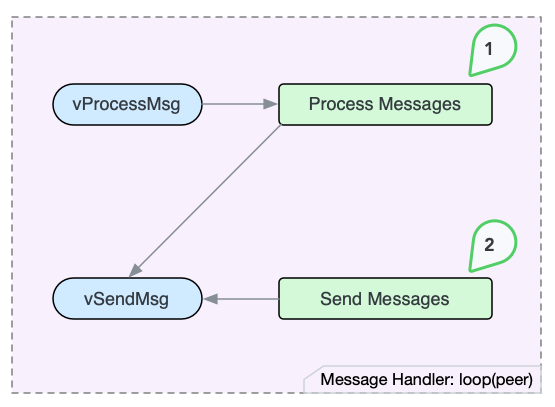
The two loops are connected at these two message queues.
Process Incoming Messages
The Message Handler Thread processes the incoming messages one by one in the function ProcessMessage with a huge switch structure.
Each peer acts as a state machine. For some reasons, the state is stored in two different locations.
- The
CNodestructure, which is passed around as a function parameter, such aspfrominProcessMessage. - The
CNodeStatestored in a global table.
Schedule more Outgoing Messages
Besides the queued messages acting as responses to the incoming messages, the Message Handler Thread also schedules more outgoing messages.
There are mainly two kinds of outgoing messages in this step:
- Messages depending on timer, either periodic or the follow ups upon time out.
- Messages queued and should be sent in batch, such as blocks and transactions announcements.
Code References
CConnman::ThreadMessageHandler: The Message Handler Thread.::ProcessMessage: This function processes a single incoming message.PeerLogicValidation::SendMessages: Check timer and batch queue and schedule more outgoing messages.